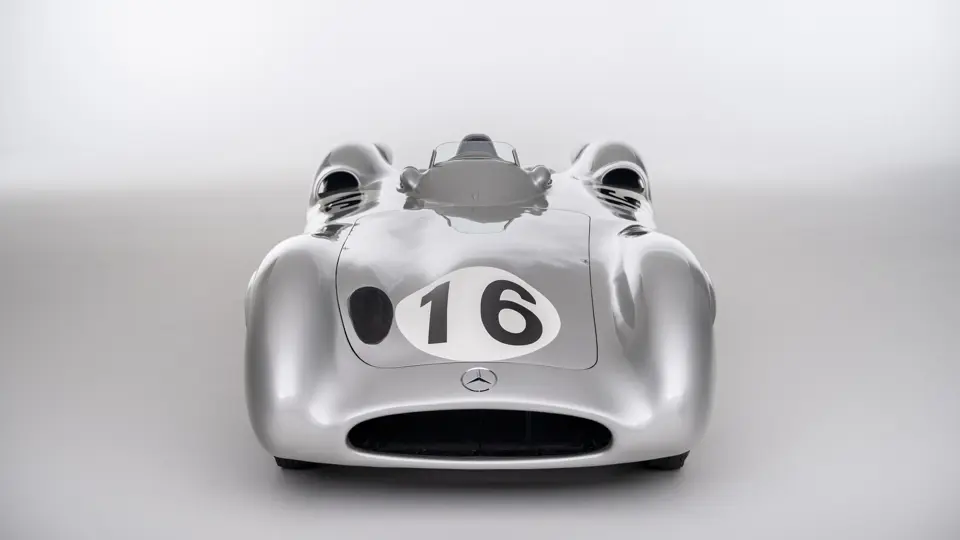
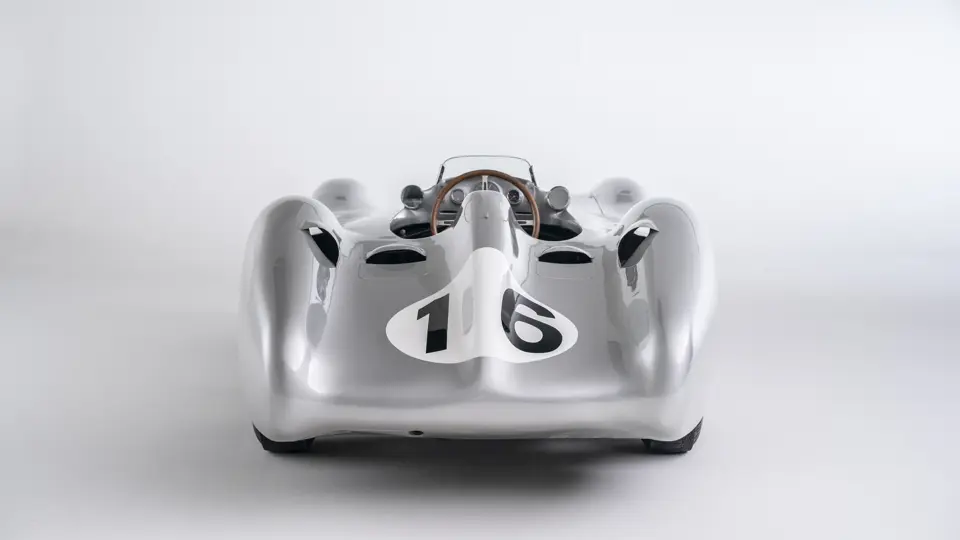
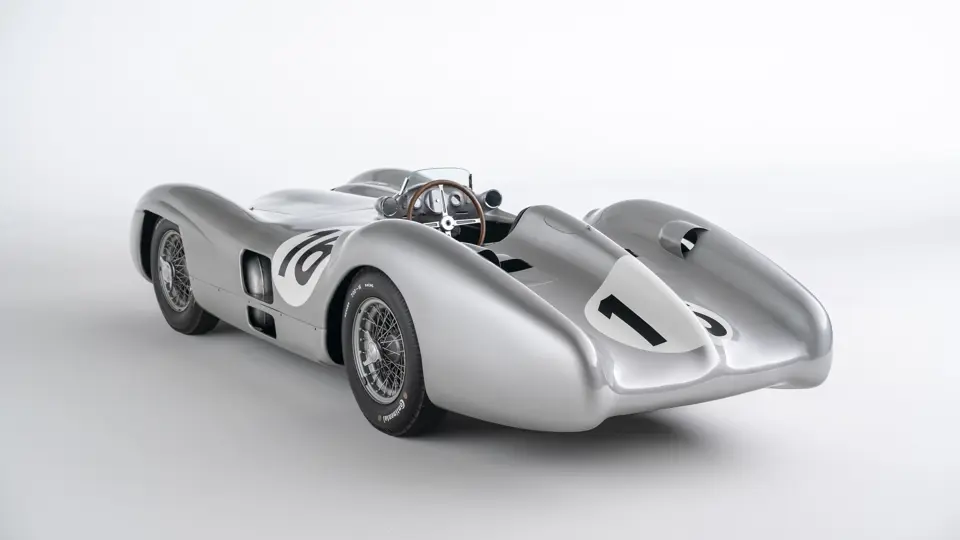
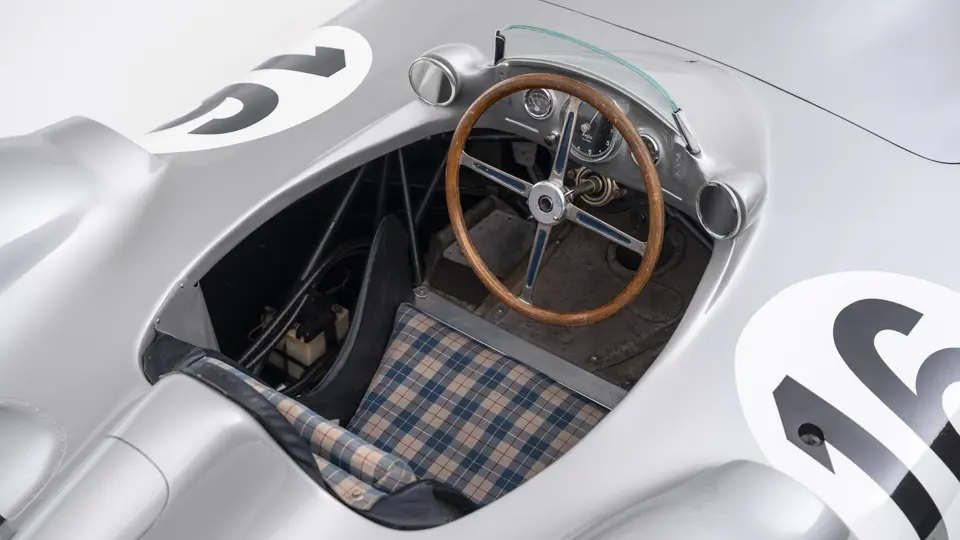
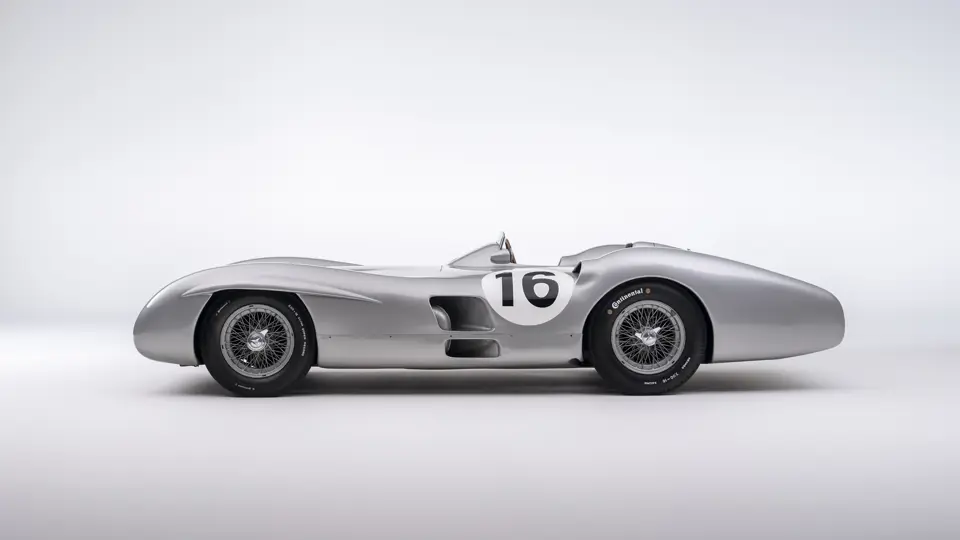
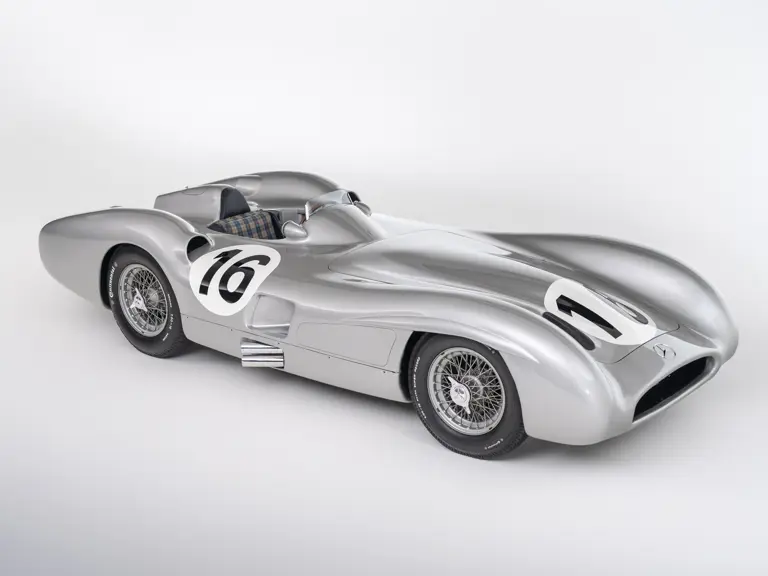
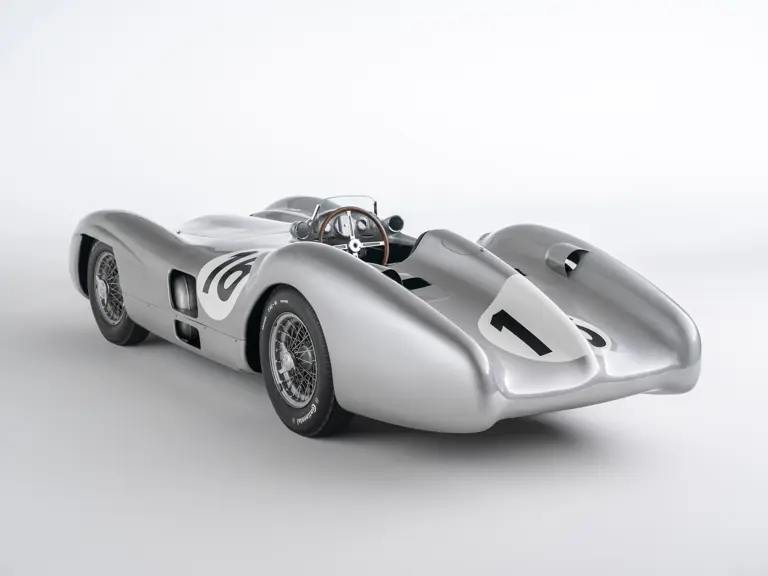
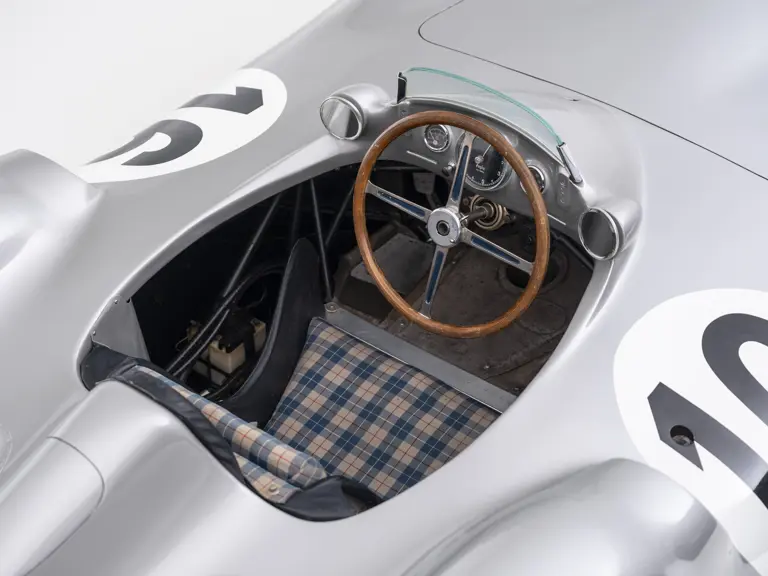
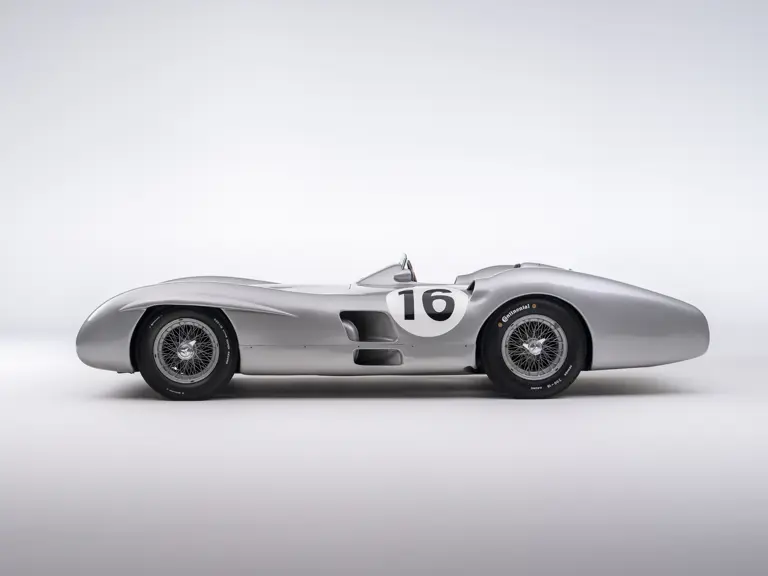
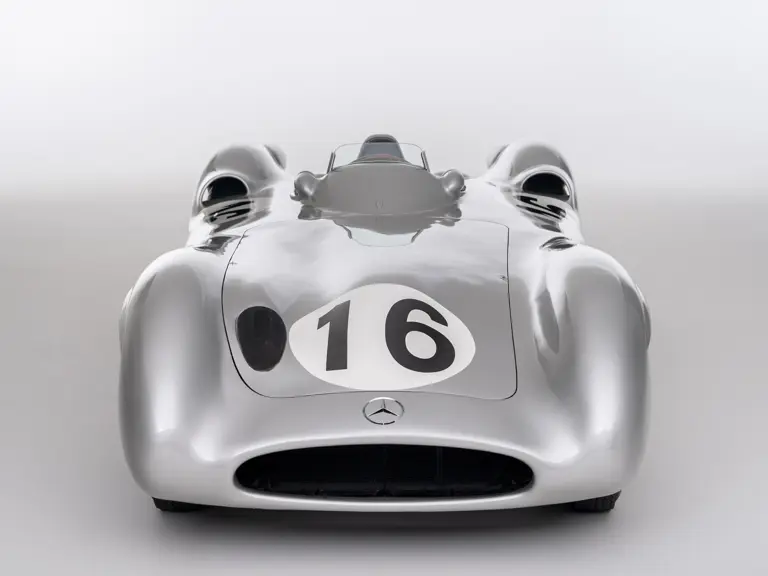
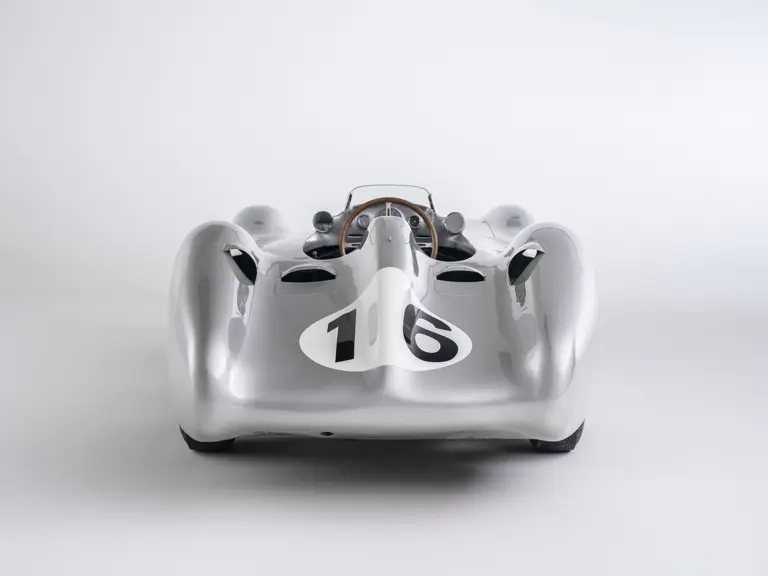
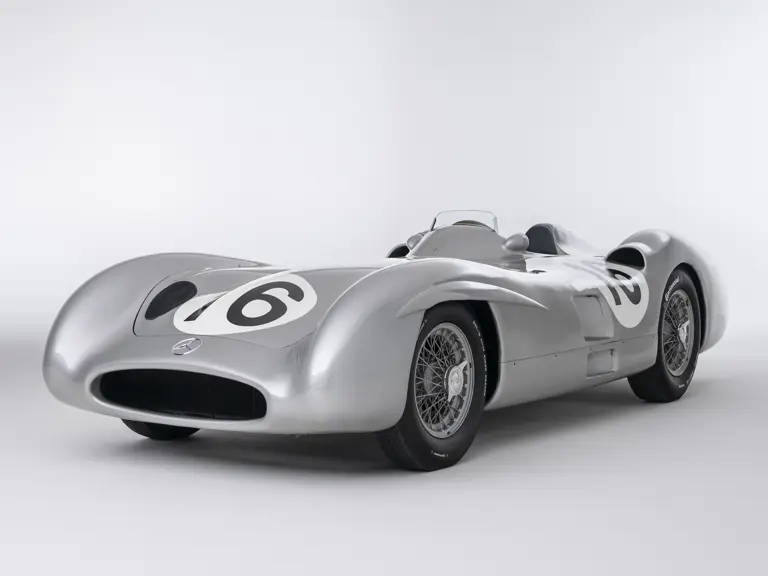
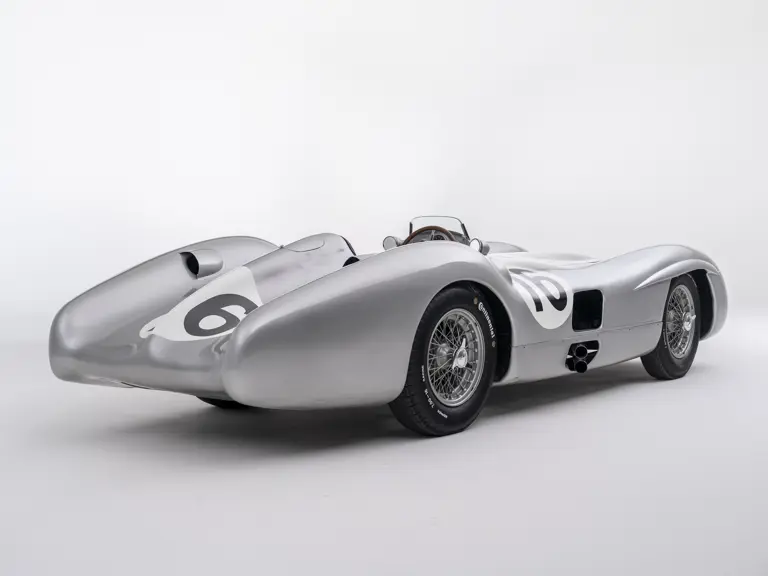
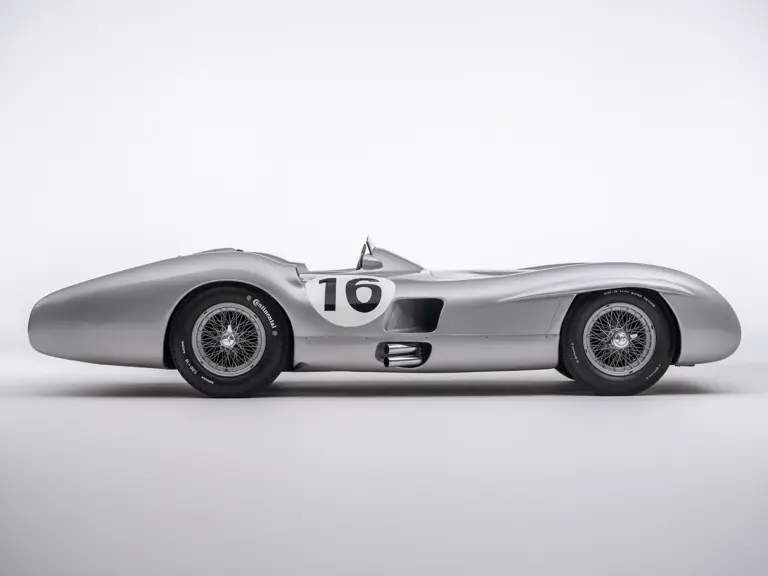
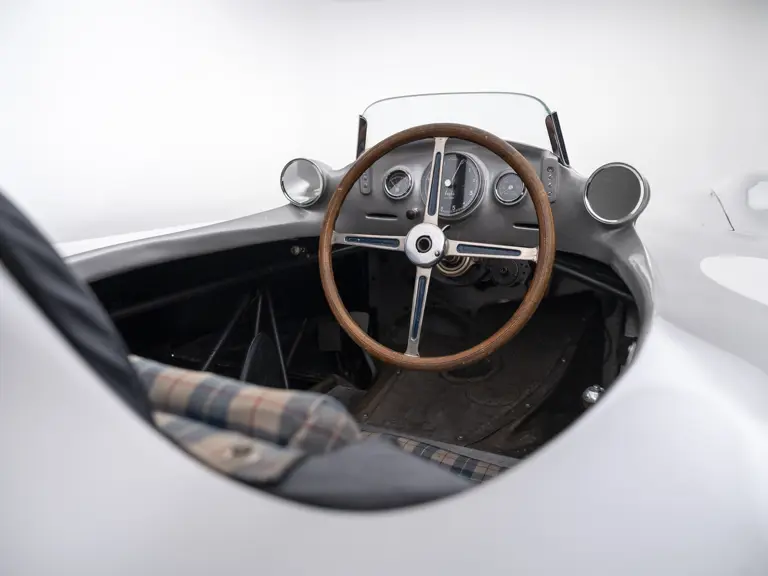
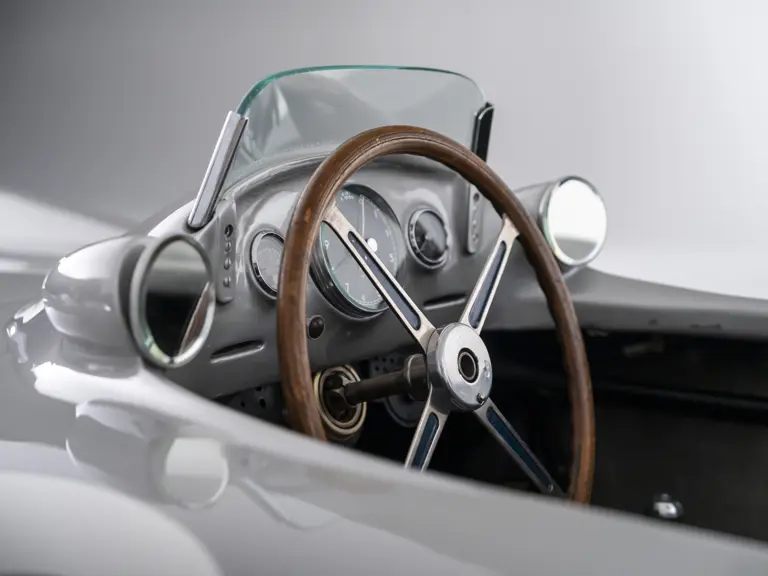
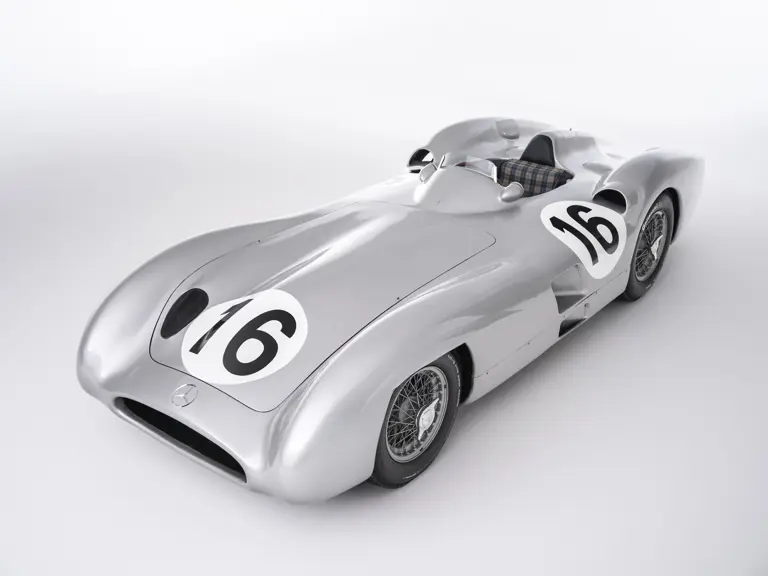
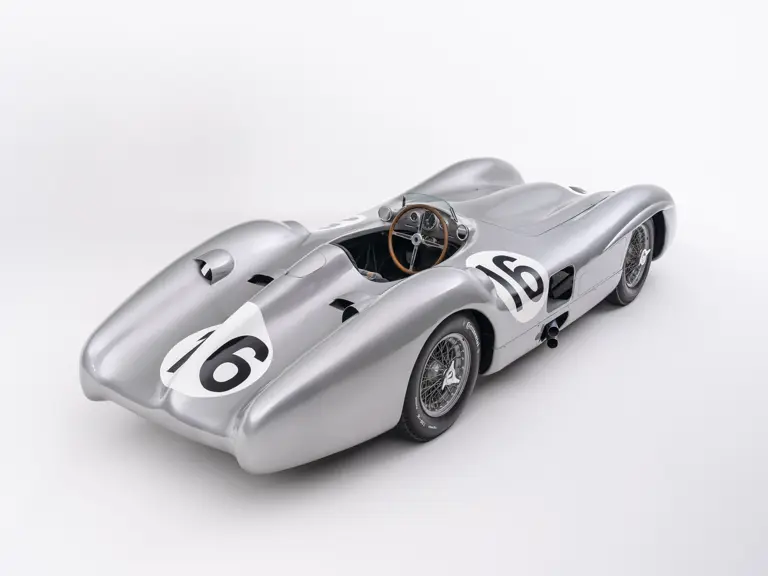
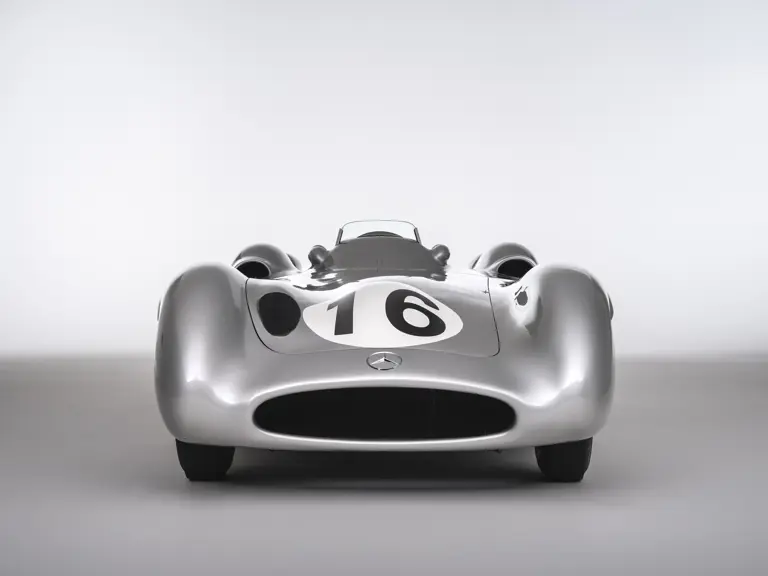
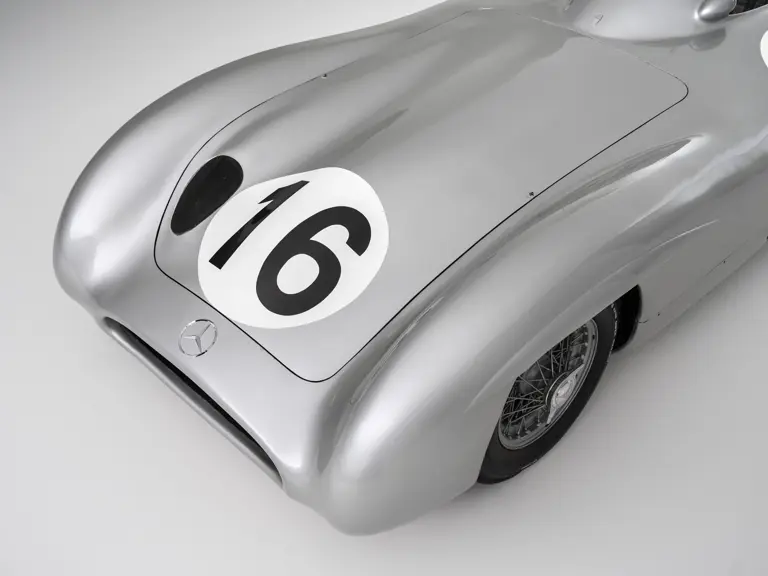
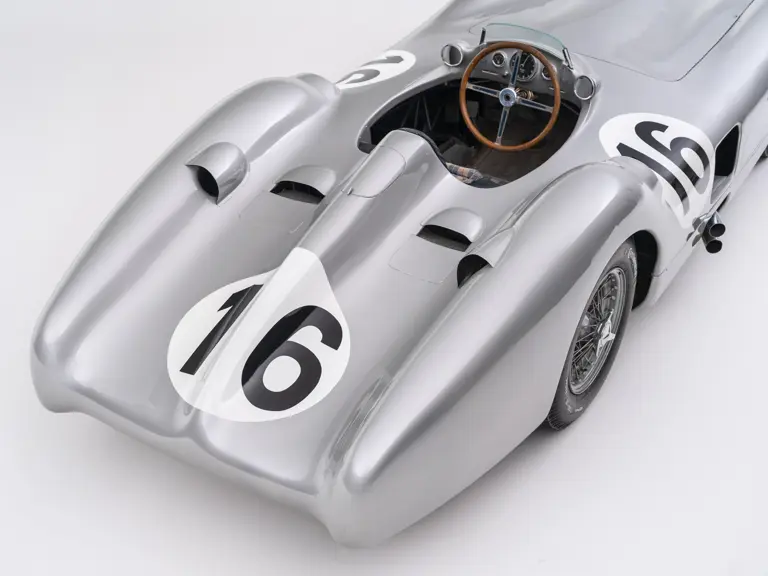
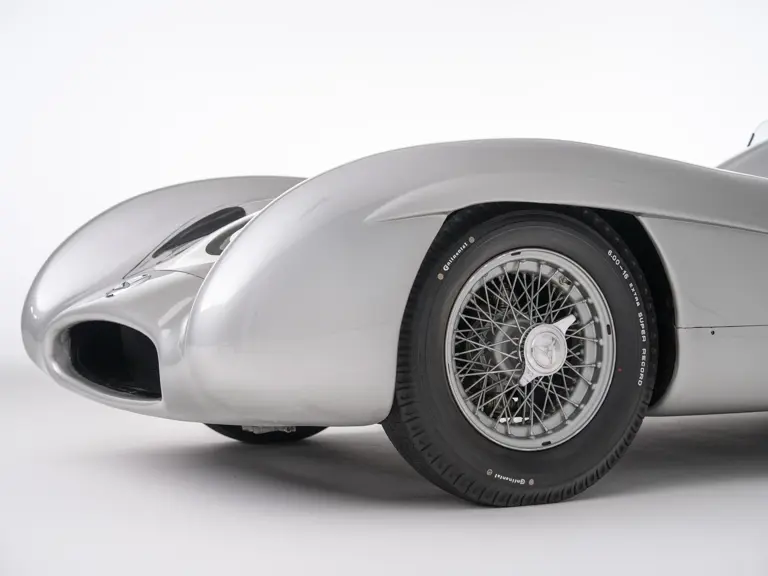
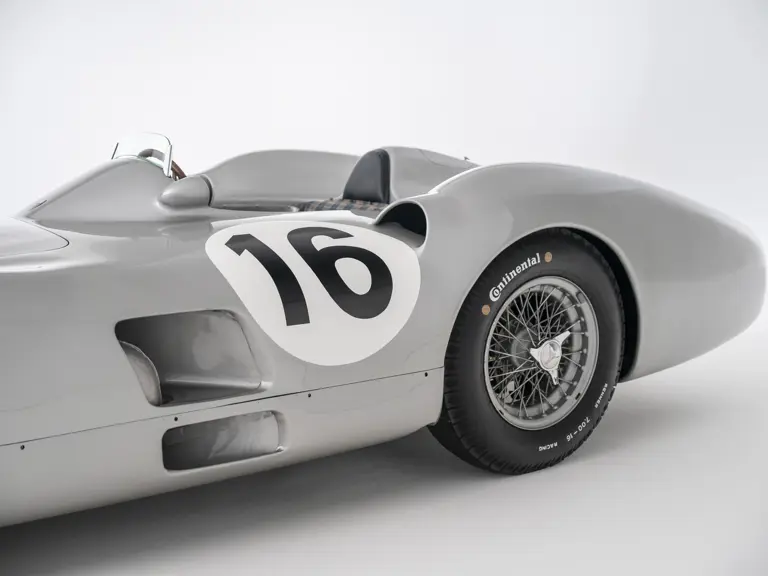
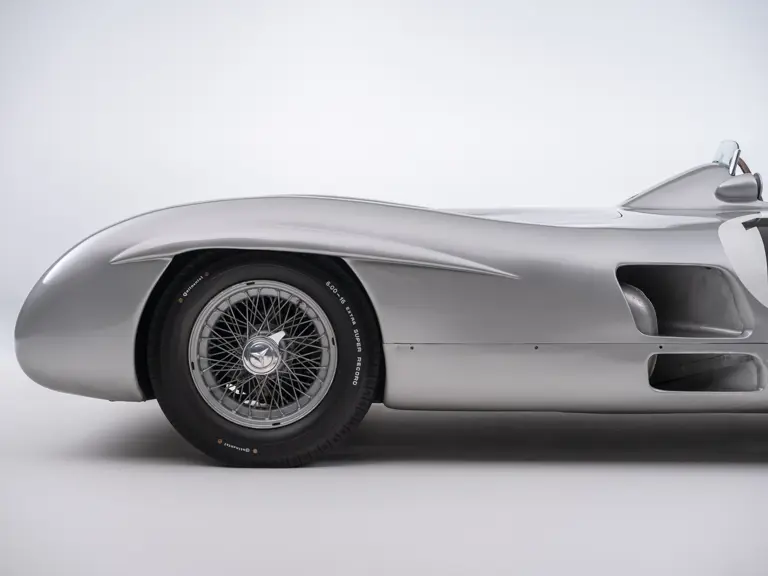
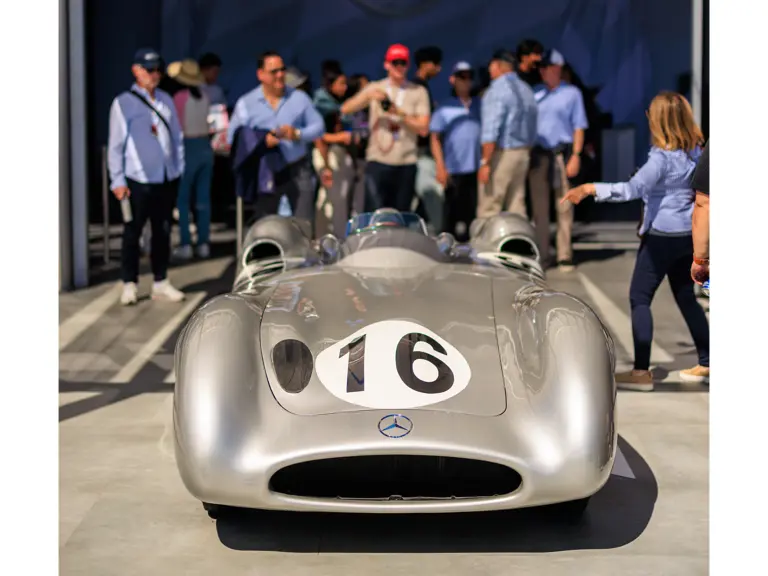
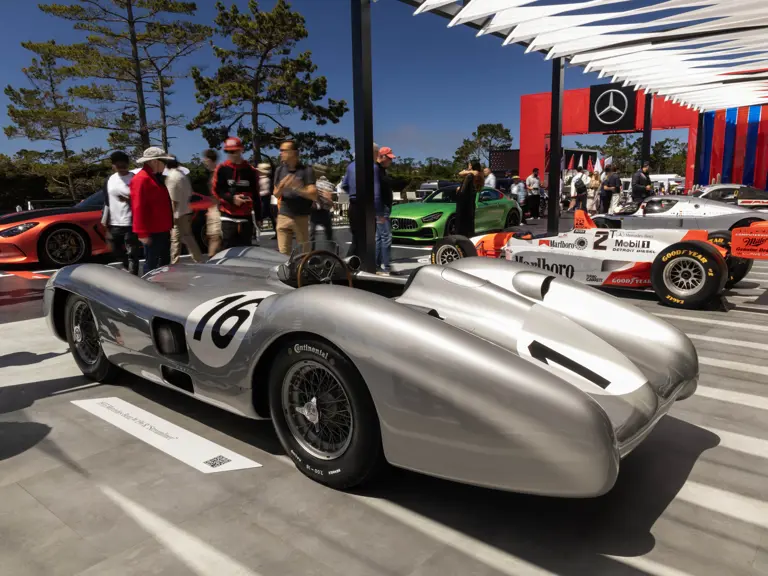
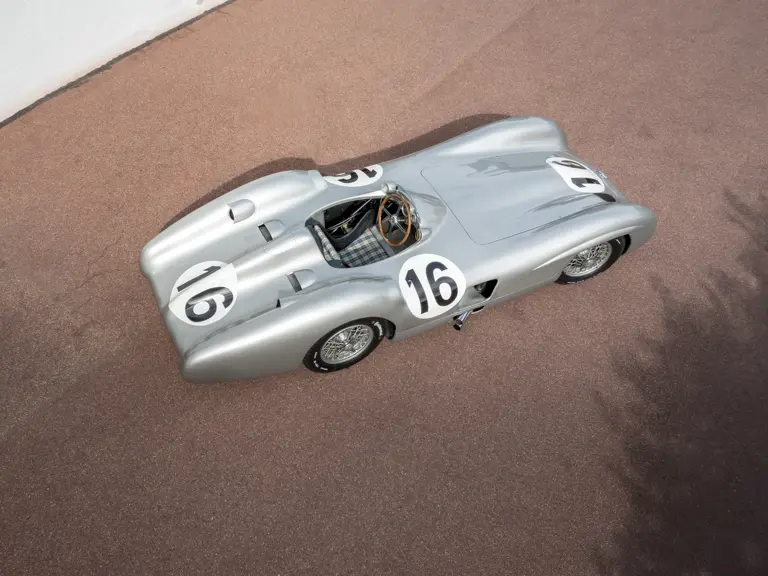
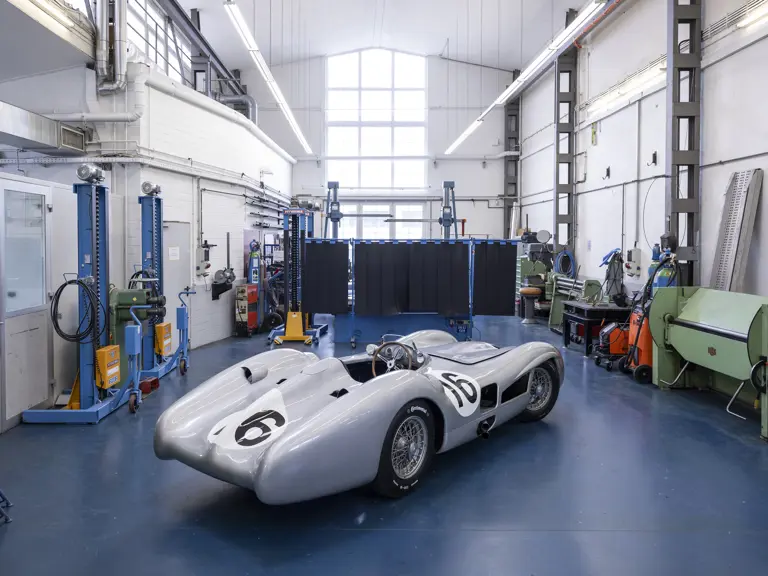
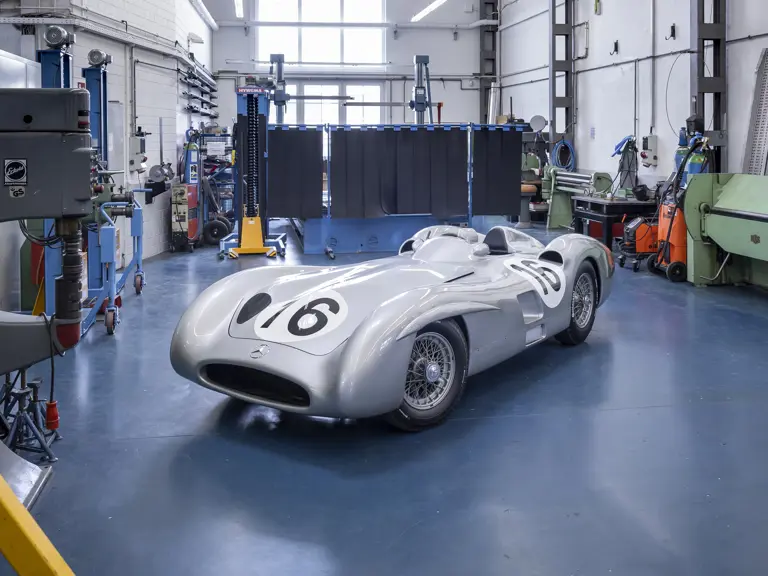
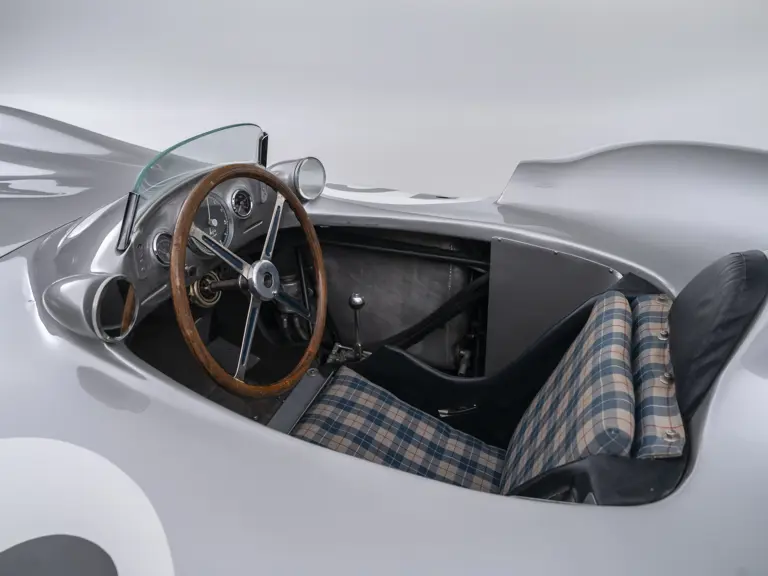
The streamlined body, in contrast, was something truly unique. Low and wide, its smoothly curved coachwork featured minimal frills, being chiefly distinguished by a wide open-mouth grille, cooling inlets on the rear shoulder haunches, and molded character lines across the tops of the front wheel wells (a design cue that came to be characteristic across the 300 SL model line, lending a marvelous continuity among the marque’s sports-racing cars). This was undoubtedly one of the most exquisite expressions of curve and stance ever pounded out, rivalling the most sensuous sports-racers and supercars for sheer visual appeal.
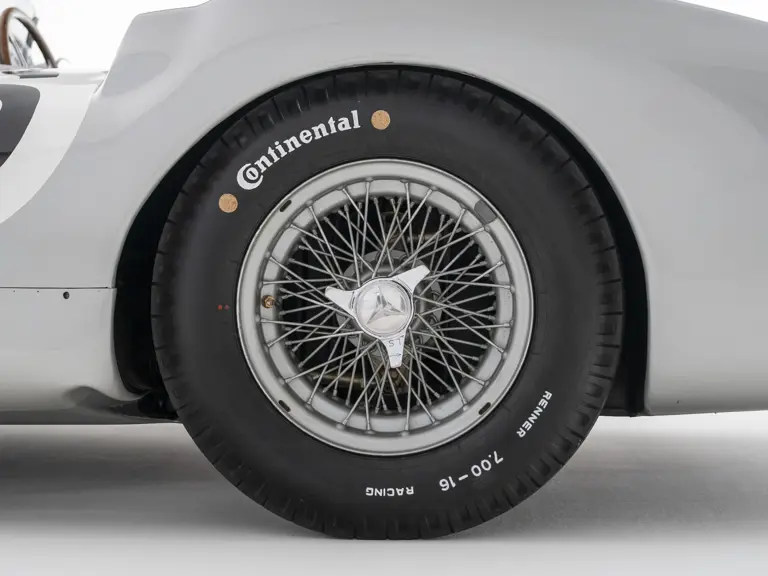
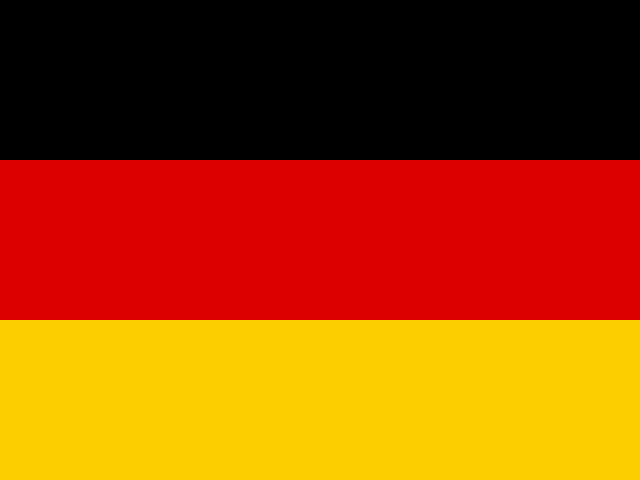
These streamlined bodies were built in extremely limited quantity by the racing department out of Elektron magnesium alloy, providing a shell even lighter than aluminum for a total weight of just over 88 pounds. The open-wheel bodies were also made of lightweight alloy, although coachwork production later shifted to steel bodies built at Sindelfingen.
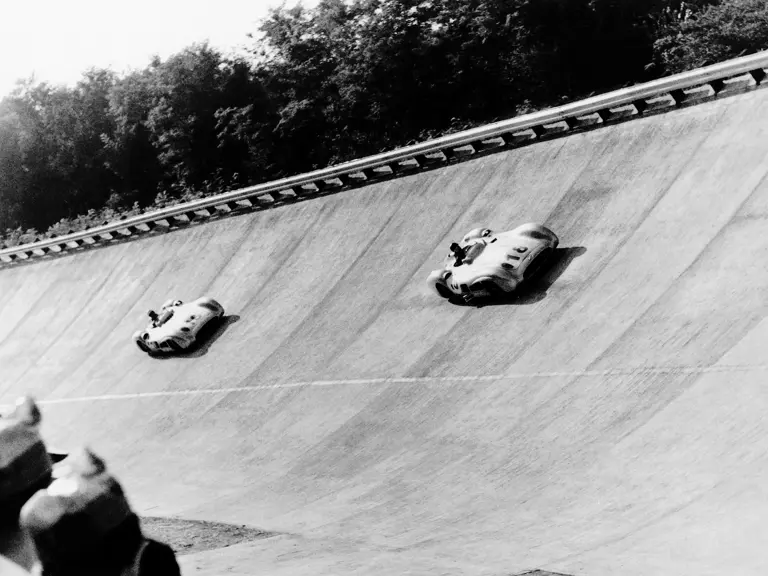
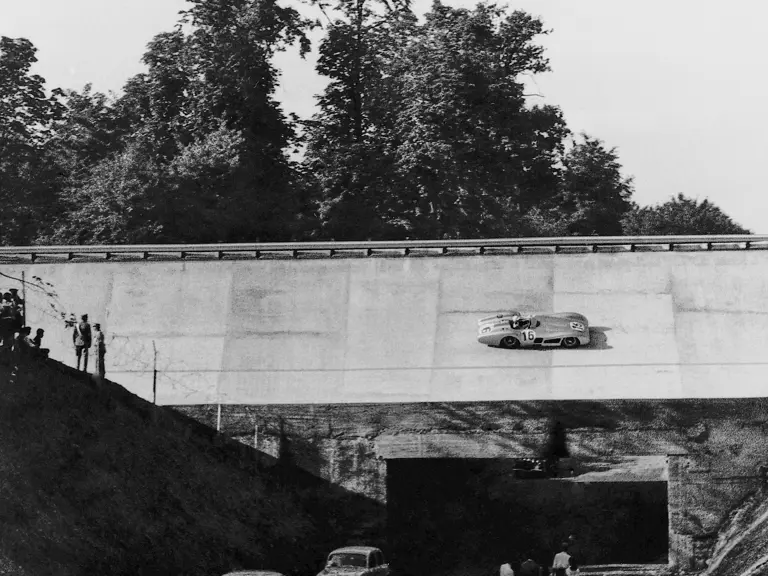
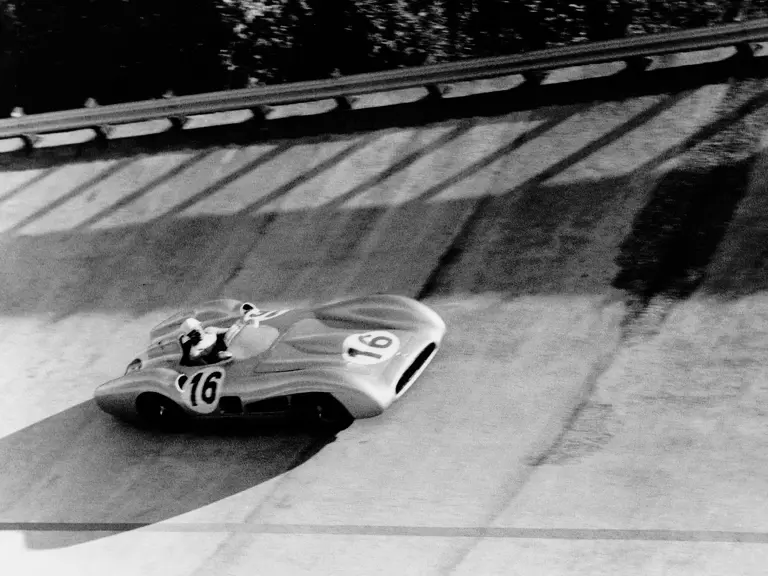
The streamlined enclosed-wheel body was intermittently campaigned with the open-wheel grand prix-style body during the 1954 and 1955 racing seasons. The factory designation for the enclosed-wheel coachwork was Stromlinie, or Streamline, and today these cars are also known as Streamliner or Stromlinienwagen (streamlined car). With such powerful mechanical specifications and slippery lightweight coachwork, the W 196 R could exceed 186 mph, making it one of the fastest grand prix cars yet constructed.
1954: A PERFECT PLAN REALIZED
Of course, Alfred Neubauer, the longtime manager of the Mercedes-Benz racing team, knew that the W 196 R’s success would be contingent on driving talent, so the decision was made early in development to contract the best array of available drivers. While two German drivers were initially signed, the veteran Karl Kling and the up-and-coming Hans Herrmann, the spotlight soon belonged to the third team member: noted Argentinian racing driver Juan Manuel Fangio.
There was a time in the late 1950s when the five-time Formula One champion Juan Manuel Fangio enjoyed a fame that transcended motorsport—when he was a true worldwide celebrity not unlike Lewis Hamilton today, and when grandstands rang out with passionate chants of “FONN-GEE-OHHH!”
Before he was a household name, in early 1954 Juan Manuel Fangio was merely a potential in transition, a burgeoning talent waiting to explode. Without a doubt, Fangio’s credentials had already been established with his first Drivers’ Championship for Alfa Romeo in 1951. But with the disintegration of the Alfa Romeo team during 1952 and the FIA’s subsequent cancelation of Formula One in favor of Formula Two proceedings, Ferrari dominated the following two years of competition. Fangio toiled away patiently with the Maserati team, and in sports car racing. Victories came repeatedly, but further championships remained elusive, and having reached his early forties, there was a justifiable presentiment among racing fans that Fangio’s best days were already behind him.
Fortunately for Fangio, his star had already been recognized by Stuttgart. Ever in search of the best driving talent, Alfred Neubauer could not help but remember Fangio’s remarkable performance in an Alfa Romeo at the 1951 Swiss Grand Prix—achieving pole, fastest lap, and a 1st-place finish. Neubauer reached out to Fangio’s agent and a contract for 1954 was signed with Mercedes-Benz. But as the 1954 season began, the new machine from Stuttgart still awaited completion. This led Fangio to continue racing for Maserati in the first two rounds of the 1954 Formula One season, winning the Grands Prix at both Argentina and Belgium. Following the Belgian Grand Prix, Fangio officially made the move to Mercedes-Benz.
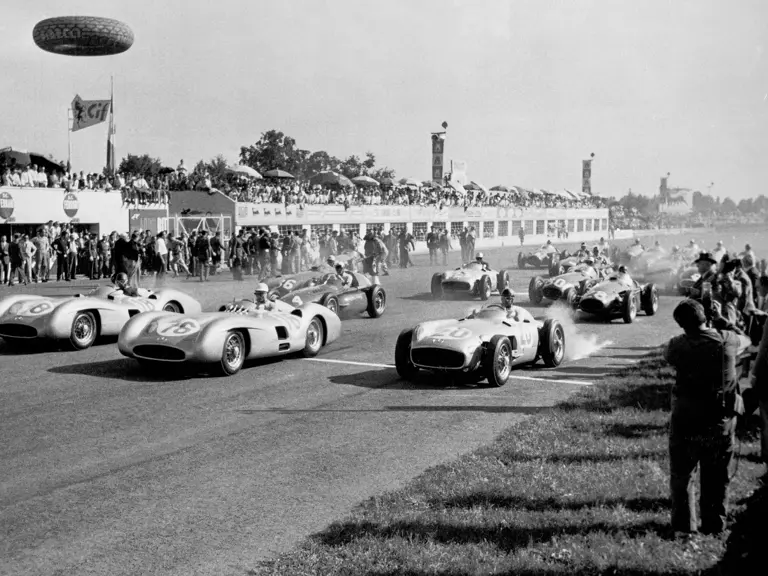
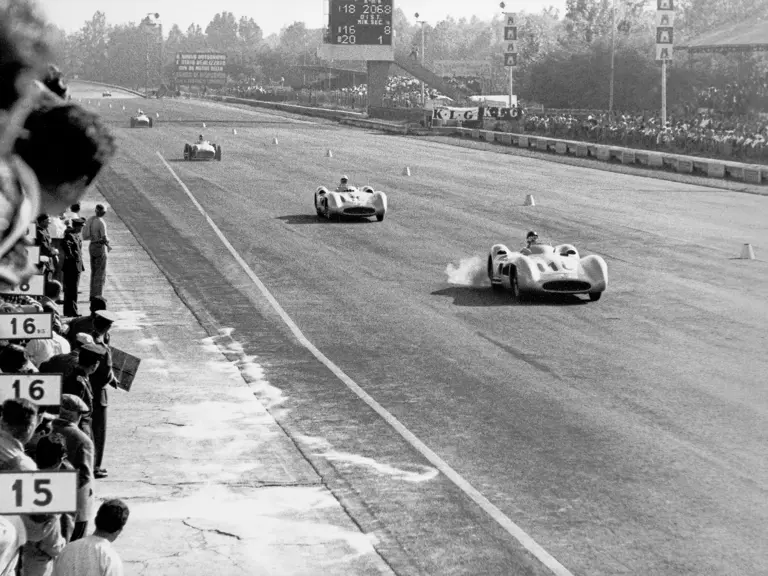
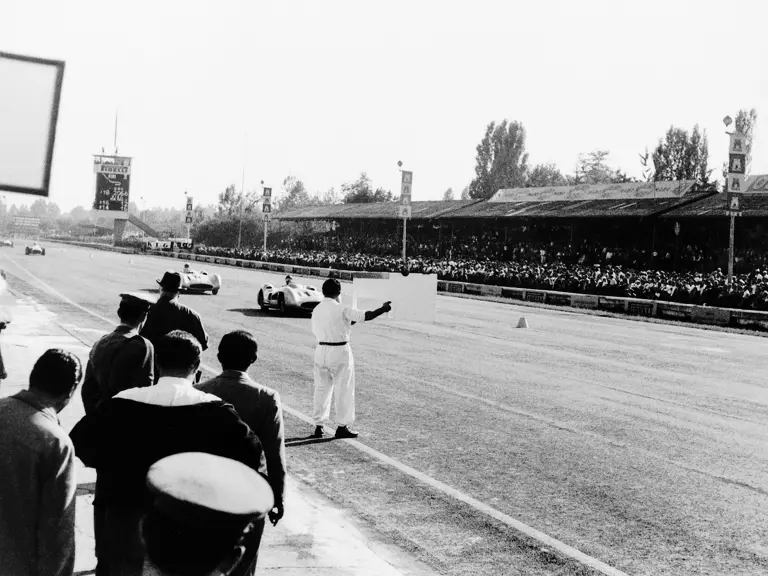
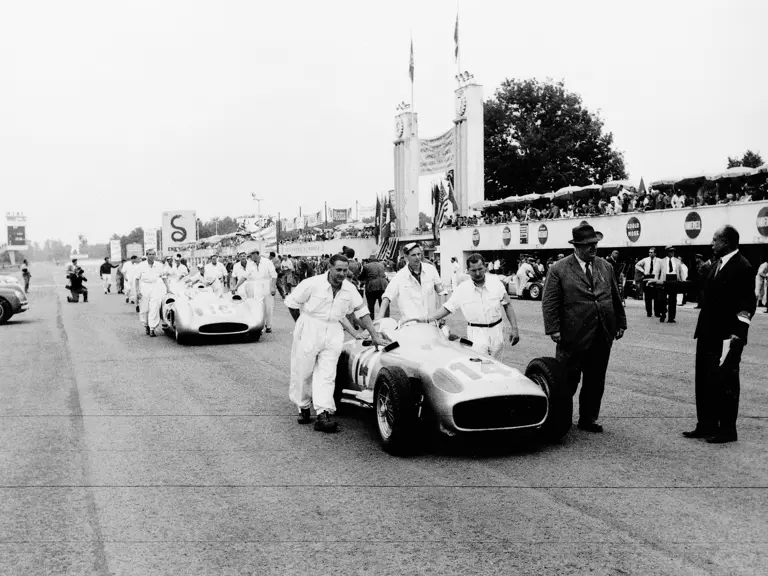
In July 1954 the new Mercedes-Benz race cars made their highly anticipated debut at the French Grand Prix at Reims. Debuting a trio of W 196 R Streamliners, their very appearance inspired awe, looking unlike anything anyone had ever seen before in a Formula One race. Team drivers Fangio, Kling, and Herrmann would qualify 1st, 2nd, and 7th, respectively. Herrmann would go on to set the race’s fastest lap while Fangio and Kling would achieve an impressive 1-2 finish. The race marked a resounding victory for Mercedes-Benz on its long-awaited return to racing.
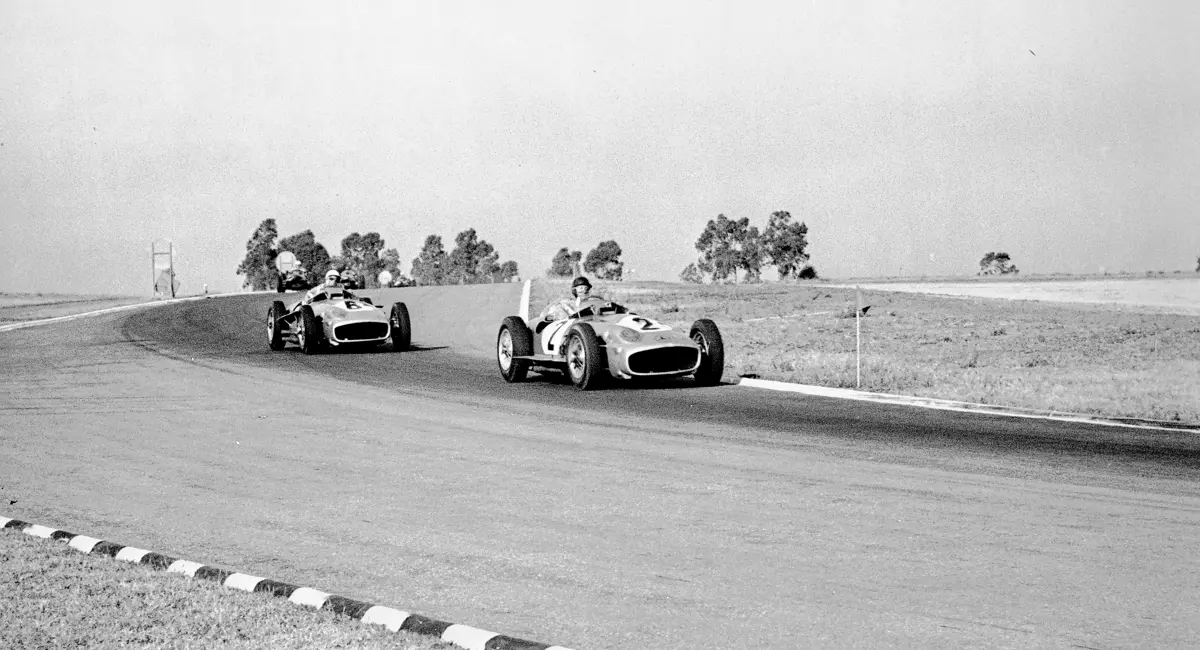
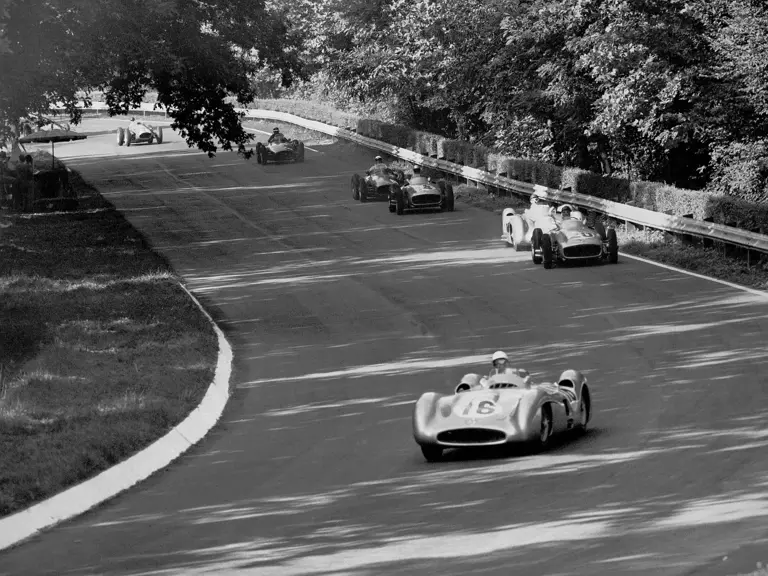
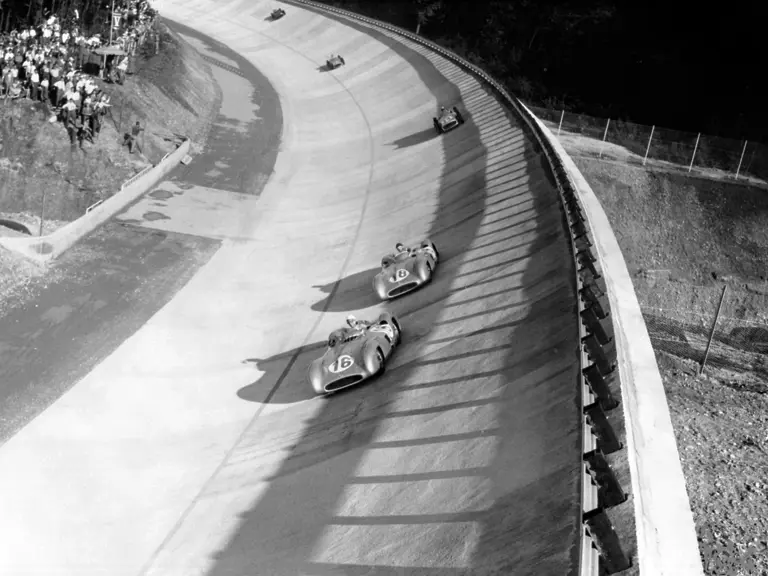
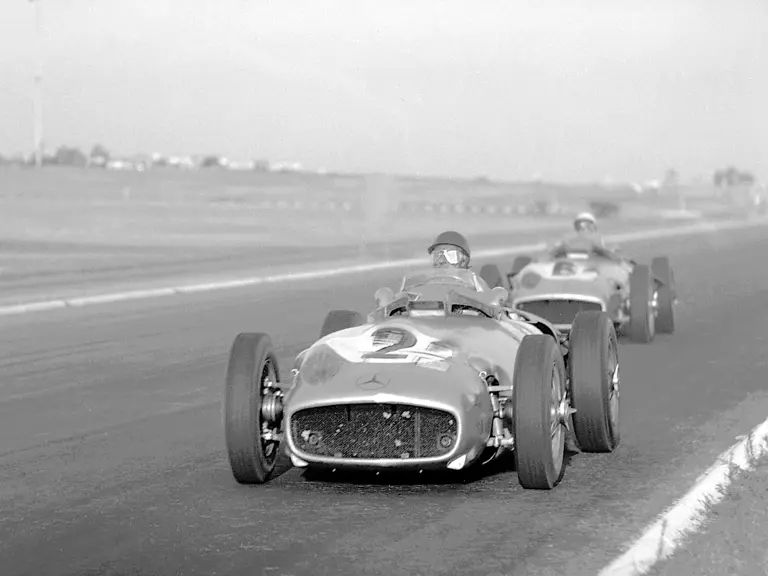
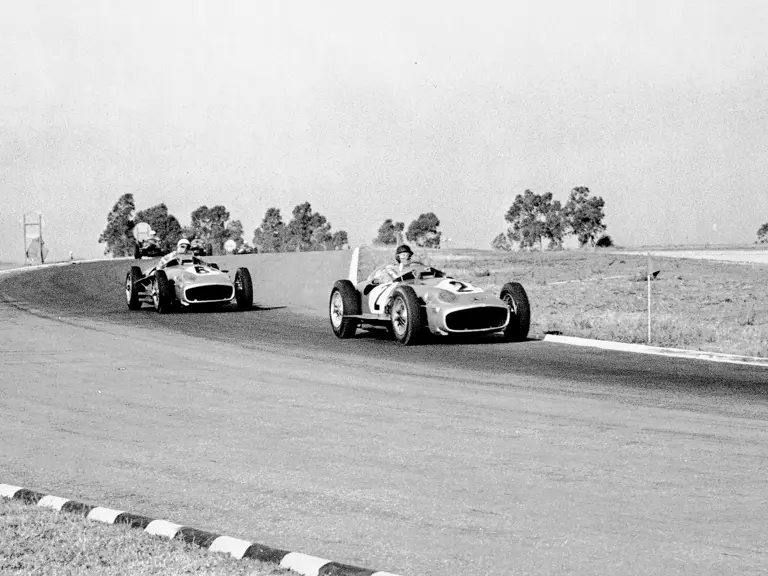
Fangio qualified for the pole position start at the British Grand Prix in late July, but rainy conditions led to a 4th-place finish. The team returned to form at the German Grand Prix at the Nürburgring in early August with a four-car team consisting of three open-wheel cars and one Streamliner. The race marked the debut of the open-wheel iteration of the W 196 R. Fangio earned pole position and would go on to win the race with Kling finishing 4th, each in open-wheel cars. A three-car team, all open-wheel, at the Swiss Grand Prix three weeks later brought nearly identical results, with Fangio again winning and Herrmann finishing 3rd.
At the Italian Grand Prix at the Monza circuit in early September, Mercedes-Benz entered two Streamliners and one open-wheel car after testing indicated that the closed-fender coachwork would be faster. In the race, a young British privateer named Stirling Moss behind the wheel of a Maserati 250F led late in the race 19 laps before retiring due to a cracked oil tank. Fangio in a Streamliner and Herrmann in an open-wheel car respectively cruised to 1st and 4th place finishes. The performance of the talented Englishman likely did not escape the attention of Rudolf Uhlenhaut and Alfred Neubauer.
Two weeks later the W 196 R cars were entered at a non-championship race, the Berlin Grand Prix, which was held at the AVUS circuit. With no points consequence, this was almost strictly a public relations demonstration for an enthusiastic German audience. Three Streamliners driven by Kling, Fangio, and Herrmann cruised to an easy 1-2-3 podium sweep.
At the Spanish Grand Prix in late October, the last race of the year, Fangio finished a team-best 3rd among a contingent of three open-wheel entries. The legend of Juan Manuel Fangio had grown; his second Drivers’ Championship was in the books. The sheer and immediate potency of the Mercedes-Benz W 196 R Silver Arrow had been established, foiling Ferrari’s attempt at a third straight Formula One championship in the process.
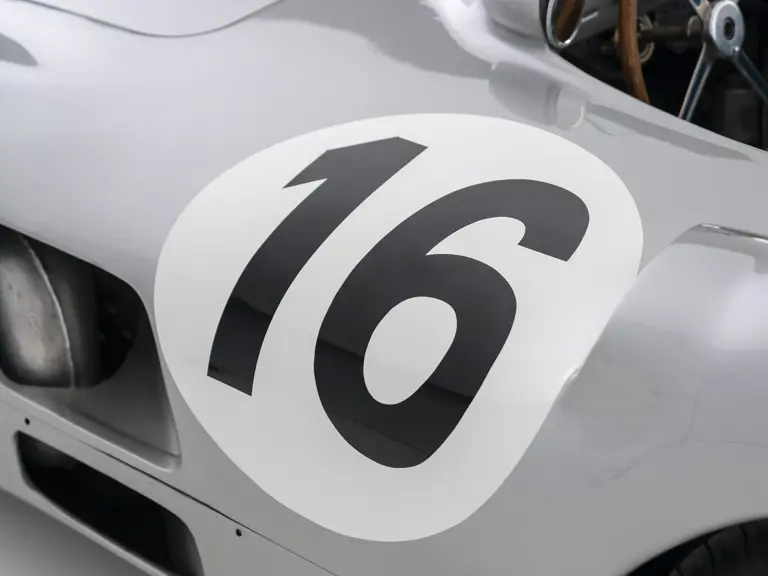
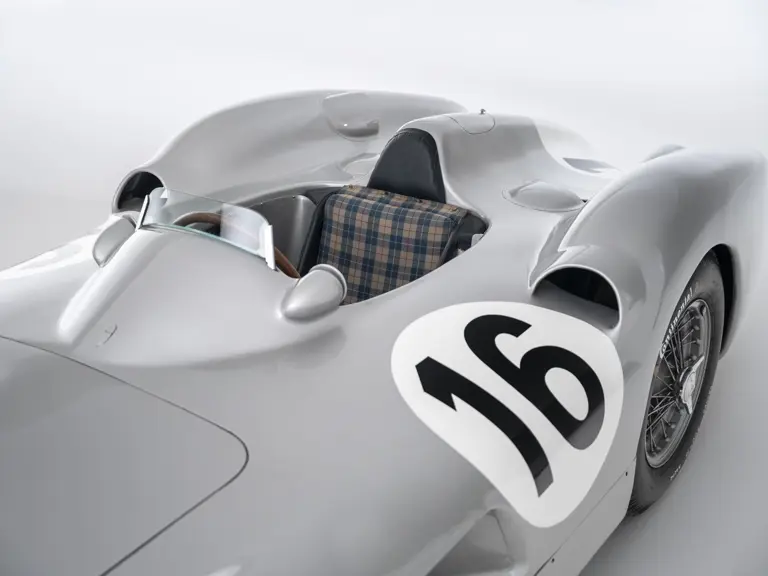
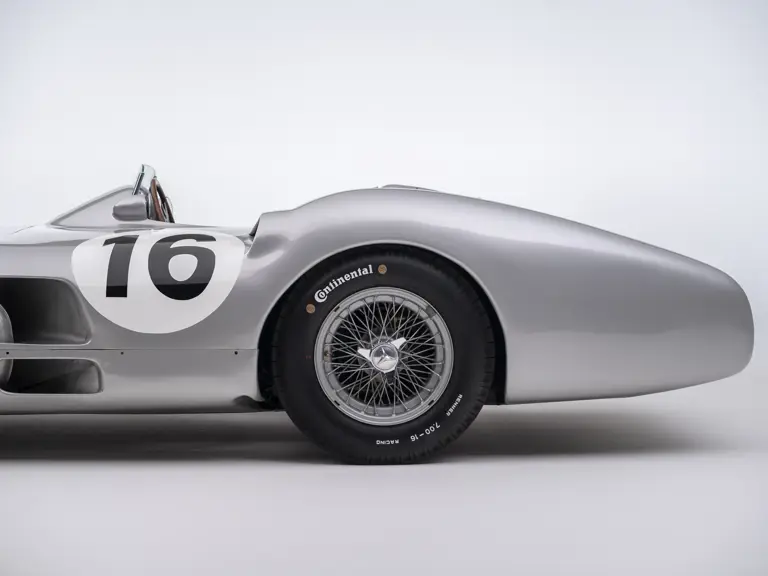
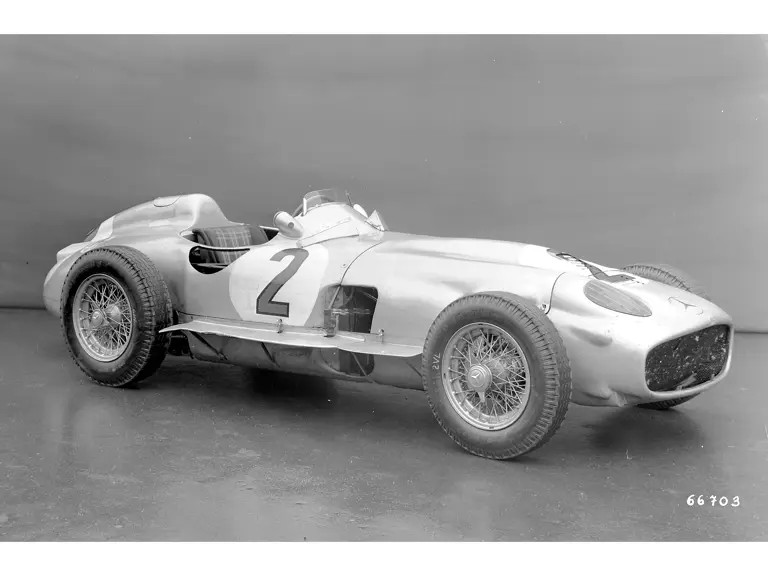
In the midst of this immediate show of dominance for the W 196 R, chassis number 00009/54, the car offered here, was completed. Originally finished as an open-wheel monoposto built on the 1954-specification 2,350-millimeter long-wheelbase chassis, and being designated with a 54 in its chassis number suffix (1955 cars have a 55 suffix), the car first began testing on 15 December 1954. For chassis number 00009/54, as well as for the victorious Mercedes-Benz racing team, even greater things were to come in the season ahead.
CHASSIS NUMBER 00009/54 IN COMPETITION: OPEN-WHEEL
For the 1955 season, the W 196 R was further developed to remain as competitive as possible. The engine was improved in numerous aspects, including the addition of a new intake manifold, and the decision was made to run the open-wheel grand prix bodies for almost all of the 1955 races. The revised cars were approximately 70 kilograms (154 pounds) lighter than their predecessors. Further testing demonstrated that the 1954 W 196 R had been significantly compromised by its Continental tires, so the rubber manufacturer was taken to task to deliver a better product, and their development during the off-season was a critical boon for the revised car.
The Rennabteilung again went after top driving talent, recruiting the upstart 25-year-old Brit from Monza, Stirling Moss, to join their stable of drivers. Moss eventually became a well-known celebrity in his own right, and one of the most famous of all the notable British drivers. Though his career would be prematurely cut short by an accident in 1962, he remained a forthright proponent of motorsports and a supporter of the automotive niche throughout his life, even serving as a brand ambassador for Mercedes-Benz in his twilight years. His lifelong contributions to the sport and Britain’s motoring niche were recognized in 2000 when he was knighted by the future King Charles.
But during the early 1950s Moss was still steadily developing as a privateer, an evolution that had begun with his win at the 1950 Tourist Trophy. To the end of securing a spot on the Mercedes-Benz team, in 1953 he bought and raced a true Formula One specification car, the Maserati 250F. Though the 250F was somewhat unreliable in competition, Moss showed considerable promise during several impressive qualifying sessions, and Neubauer took note after the events of the 1954 Italian Grand Prix. By December 1954 Moss was hired and practicing in the W 196 R, familiarizing himself with the car’s nuances while marveling at the Rennabteilung’s team environment.
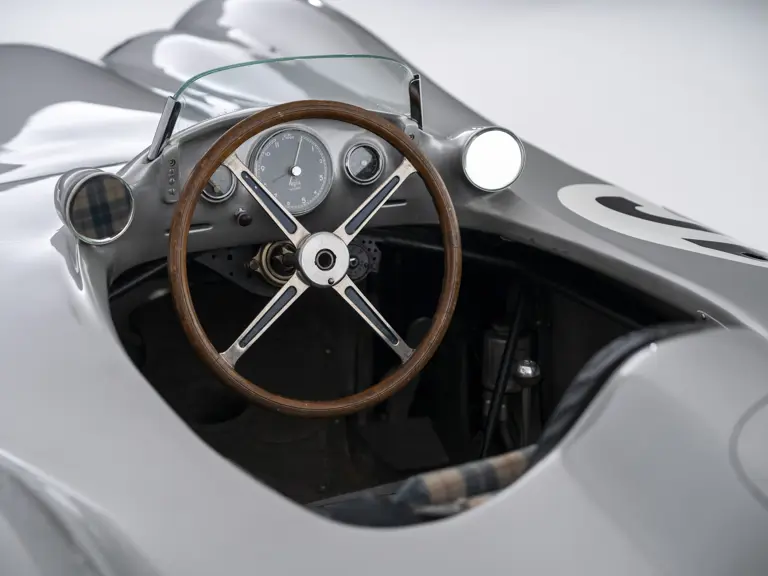
Moss later wrote of the Mercedes-Benz team, “Their thoroughness and thoughtfulness amazed me from the very beginning. It was like being in a different world…Every course where the cars raced was analyzed mathematically…Neubauer himself used to mark and time gearchanges, lap after lap…Drivers were listened to and respected, which often doesn’t happen on other top teams…Nothing was too much trouble—and they were willing to try anything which might improve performance.”
There was no doubt that Mercedes-Benz’ commitment had come to fruition in 1954, and it was about to bear further fruit with Moss onboard. It was Fangio, however, that set the winning tone with a victory at round one of the 1955 Formula One season at the Argentine Grand Prix on 16 January 1955. Since the next Formula One points event on the calendar didn’t arrive until late May, the team remained in Argentina to conduct some live-action testing during the Buenos Aires Grand Prix, as the Formula Libre race’s lack of regulations proved to be a popular testbed for Formula One teams.
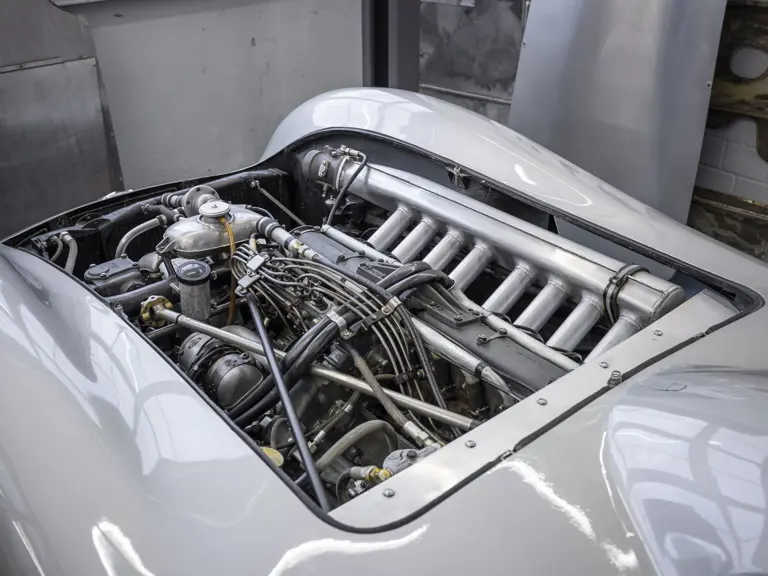
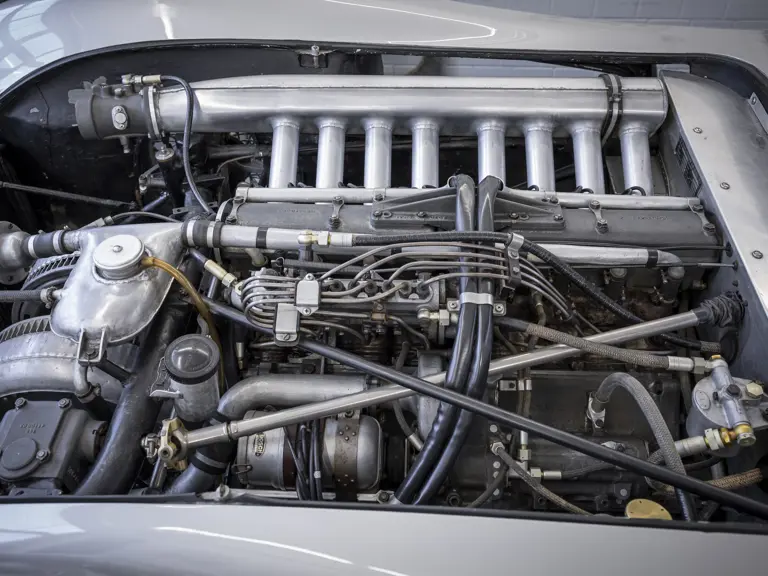
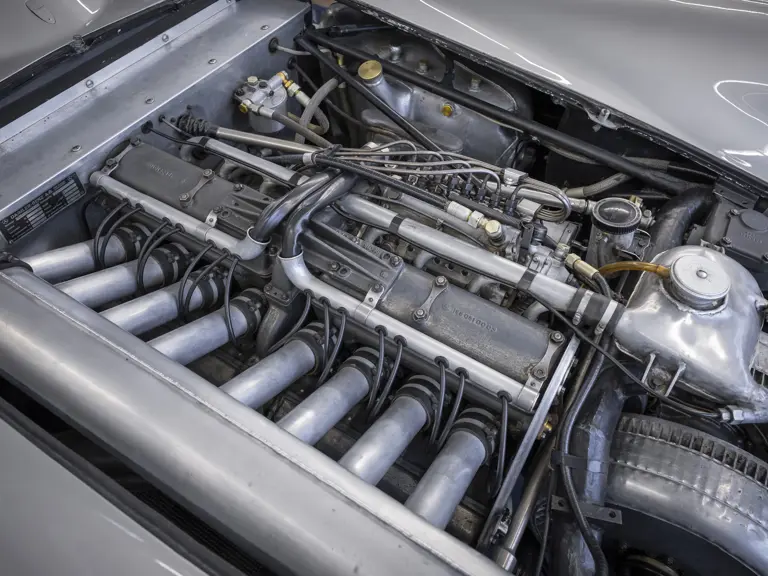
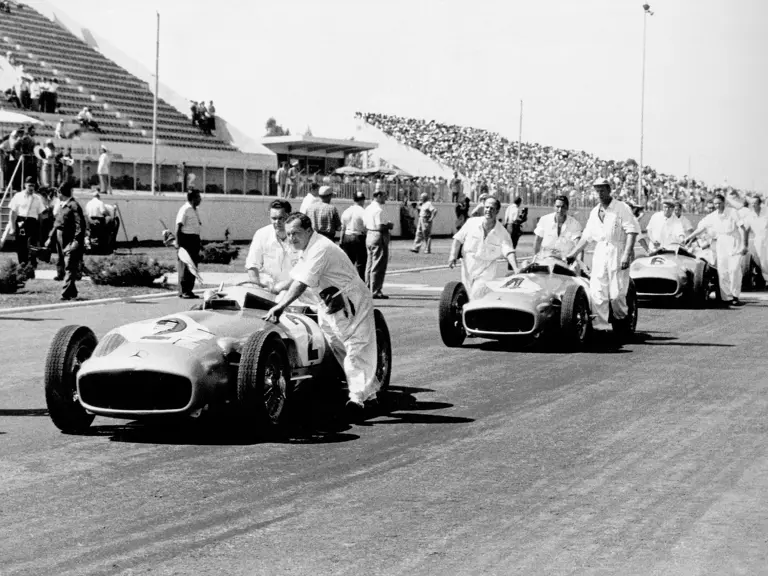
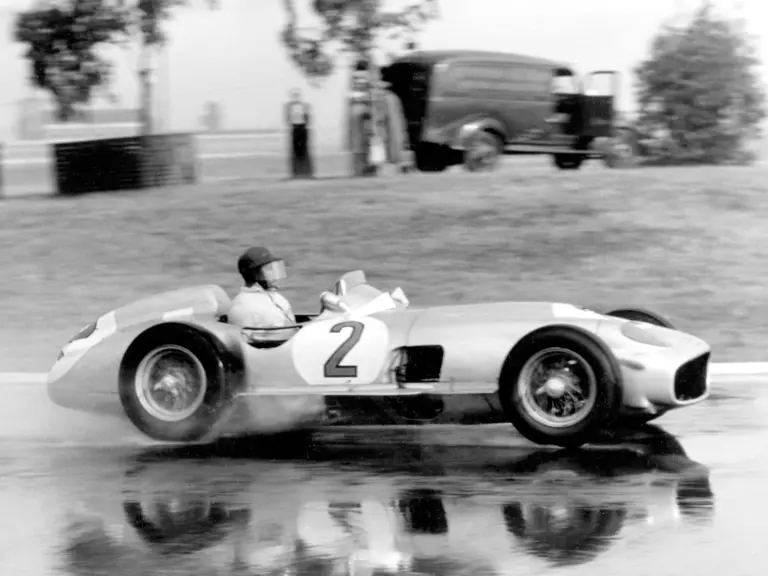
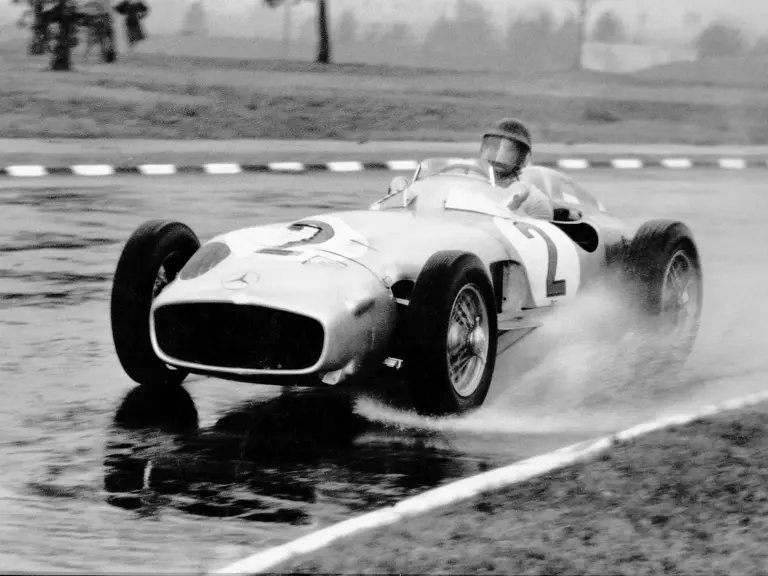
The Formula Libre Buenos Aires Grand Prix on 30 January 1955 would mark the first race for the car on offer, chassis number 00009/54, piloted by none other than Juan Manuel Fangio as car #2. According to Rennabteilung build sheets on file, as well as recent confirmation by Mercedes-Benz, chassis number 00009/54 was equipped with a “Sport 59” engine, apparently code for the 3.0-liter M196 engine, and fitted with an open-wheel monoposto body. One of the team’s primary objectives for this non-Formula One event was apparently to test this new development of the M196 engine, which was positioned for use in the upcoming W 196 S sports car, the 300 SLR. Moss, Kling, and Herrmann joined Fangio—each racing an open-wheel car.









































































 | Stuttgart, Germany
| Stuttgart, Germany



















































































